>SAUDI ARABIA HAS DECLARED WAR AGAINST IRAN AND LEBANON
https://twitter.com/IdeologyWars/status/927648891524202496 (LEBANON)
https://twitter.com/IdeologyWars/status/927606167118921728 (IRAN)
>NORTH KOREA PREPARING MISSILE LAUNCH/NUKE TEST FOR TRUMP VISIT TO SK
https://twitter.com/bowden_jayden/status/927660516419481600
>7 FUCKING CARRIERS DEPLOYED BY USA
https://twitter.com/DEFCONWSALERTS/status/927634975465328641
>3 CARRIER JOINT DRILLS NEXT TO NK IN A FEW DAYS
https://twitter.com/willripleyCNN/status/927657966576242688
>ISRAEL LARGEST EVER WAR DRILLS TO PREPARE FOR "EXTREME COMBAT SCENARIO"
https://twitter.com/EndGameShowWW3/status/927654081967116289
/mlpol/ - My Little Politics
Archived thread
Holy shit. if this is to be trusted, then the end is definitely near and shit will hit the fan. Only time will tell however, and am still a bit questioning since it's all sourced from posts on (((twitter))). If you can find some other sources to back it, then by all means post them.
1510012856.webm (2.6 MB, Resolution:1280x720 Length:00:00:23, dde847073d10c08c13cb4cd99….webm) [play once] [loop]

DO IT YOU PUSSIES BRING ON WW3 MY BODY READY!
To cool ya all off:
>SAUDI ARABIA HAS DECLARED WAR AGAINST IRAN AND LEBANON
Just a shittalk to provoke Iran
>NORTH KOREA PREPARING MISSILE LAUNCH/NUKE TEST FOR TRUMP VISIT TO SK
Another flexing from Little Rocketman that will fail
>7 FUCKING CARRIERS DEPLOYED BY USA
>3 CARRIER JOINT DRILLS NEXT TO NK IN A FEW DAYS
Wow, Kim! Look at my toys! And they are bigger than yours.
>ISRAEL LARGEST EVER WAR DRILLS TO PREPARE FOR "EXTREME COMBAT SCENARIO"
OY VEY! We dindu nuffin ,ebil Majoosi wants to destroy us (God I hope they do u fuckin kikes)
So calm your tits, it's not happening.
It never does.
>SAUDI ARABIA HAS DECLARED WAR AGAINST IRAN AND LEBANON
Just a shittalk to provoke Iran
>NORTH KOREA PREPARING MISSILE LAUNCH/NUKE TEST FOR TRUMP VISIT TO SK
Another flexing from Little Rocketman that will fail
>7 FUCKING CARRIERS DEPLOYED BY USA
>3 CARRIER JOINT DRILLS NEXT TO NK IN A FEW DAYS
Wow, Kim! Look at my toys! And they are bigger than yours.
>ISRAEL LARGEST EVER WAR DRILLS TO PREPARE FOR "EXTREME COMBAT SCENARIO"
OY VEY! We dindu nuffin ,ebil Majoosi wants to destroy us (God I hope they do u fuckin kikes)
So calm your tits, it's not happening.
It never does.
>>86254
>SAUDI ARABIA HAS DECLARED WAR AGAINST IRAN AND LEBANON
Good. I hope they wipe each other out.
>SAUDI ARABIA HAS DECLARED WAR AGAINST IRAN AND LEBANON
Good. I hope they wipe each other out.
>>86254
>ISRAEL LARGEST EVER WAR DRILLS TO PREPARE FOR "EXTREME COMBAT SCENARIO"
wonder how many tanks they'll break this time.
>ISRAEL LARGEST EVER WAR DRILLS TO PREPARE FOR "EXTREME COMBAT SCENARIO"
wonder how many tanks they'll break this time.
Looks like NYT made a write up on the situation.
https://archive.is/pkhWF
>We see this as an act of war,” the Saudi foreign minister, Adel Jubair, said in an interview on CNN. “Iran cannot lob missiles at Saudi cities and towns and expect us not to take steps"
>>86309
>>86311
I was thinking more the Saudis than anything else. Lebanon is alright, I guess.
https://archive.is/pkhWF
>We see this as an act of war,” the Saudi foreign minister, Adel Jubair, said in an interview on CNN. “Iran cannot lob missiles at Saudi cities and towns and expect us not to take steps"
>>86309
>>86311
I was thinking more the Saudis than anything else. Lebanon is alright, I guess.
How can Saudi Arabia even declare war if they can't even keep their government in check?
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/second-saudi-prince-confirmed-killed-during-crackdown
>Following the death of Prince Mansour bin-Muqrin in a helicopter crash near the Yemen border yesterday, the Saudi Royal Court has confirmed the death of Prince Abdul Aziz bin Fahd - killed during a firefight as authorities attempted to arrest him.
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/second-saudi-prince-confirmed-killed-during-crackdown
>Following the death of Prince Mansour bin-Muqrin in a helicopter crash near the Yemen border yesterday, the Saudi Royal Court has confirmed the death of Prince Abdul Aziz bin Fahd - killed during a firefight as authorities attempted to arrest him.
>>86320
>The Saudi Royal family has now lost two princes in 24 hours
Now with the possibility of a hot war, how many Saudi princes are going to die by the end of the week? By the end of the month?
>The Saudi Royal family has now lost two princes in 24 hours
Now with the possibility of a hot war, how many Saudi princes are going to die by the end of the week? By the end of the month?
It's never habbening.
>>86375
The Saudis say they have been declared war on. The Iranians aren't exactly taking a hard stance yet. Tensions are hot right now. Either someone pulls a trigger, or the tensions slowly dissipate.
The Saudis say they have been declared war on. The Iranians aren't exactly taking a hard stance yet. Tensions are hot right now. Either someone pulls a trigger, or the tensions slowly dissipate.

I predict it won't go farther than this, but instability in the Saudi regime may continue to fester. This is a mere move of desperation.
1510034145.png (639.8 KB, 1756x1450, 66827887c8d6bcbfbff0d058d6….png)
>>86330
>>86392
With that being the case, my little Semitic lizard brain got to thinking, how can we benefit from all this financially? I remember reading a few posts on 8/pol/ that suggested that Anons purchase the Iraqi Dinar, suggesting that as Saudi goes to Hell the Iraqis are going to start picking up their slack in oil production, and with their exports going up, their currency will revalue (one Anon even suggested that the stockpile he managed to gather may come to be worth millions in US dollars).
Now with that being said, I've spoken to one person at my local bank so far, an investment broker (I think, I can't remember his actual title), and he advised against the purchase, stating that because Iraq is currently using the US dollar for it's day-to-day business, the revaluing of the Dinar would mean that something's gone horribly wrong with the US currency.
I'm not sure who's advice I want to go with, could this be a smart investment? If it is, where is a good place to get the stuff without getting fleeced or having your money eaten? Most, if not all major banking institutions here in Canadistan don't trade the stuff, and roadside currency exchanges have shitty rates (if you can even find one that has it). Obviously, even if Anon is right, no one can expect to get rich quick off of this, especially knowing that Iraq's infrastructure hasn't been completely rebuilt yet.
>>86392
With that being the case, my little Semitic lizard brain got to thinking, how can we benefit from all this financially? I remember reading a few posts on 8/pol/ that suggested that Anons purchase the Iraqi Dinar, suggesting that as Saudi goes to Hell the Iraqis are going to start picking up their slack in oil production, and with their exports going up, their currency will revalue (one Anon even suggested that the stockpile he managed to gather may come to be worth millions in US dollars).
Now with that being said, I've spoken to one person at my local bank so far, an investment broker (I think, I can't remember his actual title), and he advised against the purchase, stating that because Iraq is currently using the US dollar for it's day-to-day business, the revaluing of the Dinar would mean that something's gone horribly wrong with the US currency.
I'm not sure who's advice I want to go with, could this be a smart investment? If it is, where is a good place to get the stuff without getting fleeced or having your money eaten? Most, if not all major banking institutions here in Canadistan don't trade the stuff, and roadside currency exchanges have shitty rates (if you can even find one that has it). Obviously, even if Anon is right, no one can expect to get rich quick off of this, especially knowing that Iraq's infrastructure hasn't been completely rebuilt yet.
1510047617_1.jpg (22.9 KB, 600x313, 2223e77ccbdf50d16b51edc21e….jpg)
1510047617_2.png (121.3 KB, 600x347, c67bb5d16c7ccda5660e621090….png)

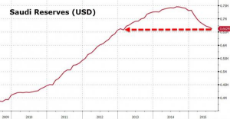
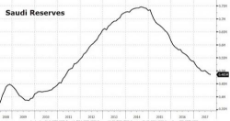
Saudi Arabia is screwed. They depend on selling oil to hold everything up. But as the economies turn down and efficiencies and technological change occurs they will not be able to continue on in the same way.
http://archive.fo/vtfB5 - ZeroHedge - S&P Downgrades Saudi Arabia On Slumping Crude, Ballooning Fiscal Deficit (See Pics)
What all this shows is that economic stress equal real life stress then murder and war. I expect due to the situation Saudi royal family is massively rearranging everything internally and externally, including some cullings.
Not archiving, too many. Links are in reverse date order.
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/saudi-arabia-about-confiscate-33-billion-four-its-richest-people
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/saudi-banks-begin-freezing-accounts-arrested-royals-block-private-jets
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/06/saudi-purge-sees-senior-princes-top-billionaire-detained/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/05/saudi-energy-minister-falih-says-concerned-about-asias-future-energy-security/
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-05/saudi-helicopter-carrying-8-high-ranking-officials-crown-prince-mansour-crashed-all-
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-05/we%E2%80%99ll-see-some-initial-panic-world-reacts-billionaire-alwaleeds-shocking-purge
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-04/shocking-purge-saudi-king-arrests-billionaire-prince-bin-talal-others-anti-money-lau
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-04/lebanon-plunges-uncertainty-after-premier-resigns-fearing-assassination-plot
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/01/saudi-arabia-may-raise-december-crude-oil-prices-to-asia-to-highest-in-few-years/
https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/international-news/middle_east/saudi-arabia-in-search-of-cash/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/10/24/russia-cements-top-spot-in-crude-sales-to-china-as-saudis-recede/
http://21stcenturywire.com/2017/10/24/syrian-victory-will-reshape-middle-east-recalibrate-global-hegemony/
http://www.thechinamoneyreport.com/2017/10/13/china-will-compel-saudi-arabia-to-trade-oil-in-yuan-and-thats-going-to-affect-the-us-dollar/ <<<<<<<<<<<<<THIS
https://gefira.org/en/2017/10/05/saudi-king-arrives-in-moscow-with-energy-syria-likely-on-agenda/
https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/markets-by-sector/energy/saudi-arabia-threatens-to-privatize-its-oil-and-exit-opec/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/09/27/saudi-arabia-sells-third-international-bond-to-raise-12-5-billion/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/08/28/china-saudi-arabia-agree-to-build-energy-cooperation-mechanisms/
http://www.thechinamoneyreport.com/2017/03/27/chinese-drone-factory-in-saudi-arabia-first-in-middle-east/ <<<<<<China again.
Enough links?
Saudi Arabia might slip the US leash and go to China as China rises.
http://archive.fo/vtfB5 - ZeroHedge - S&P Downgrades Saudi Arabia On Slumping Crude, Ballooning Fiscal Deficit (See Pics)
What all this shows is that economic stress equal real life stress then murder and war. I expect due to the situation Saudi royal family is massively rearranging everything internally and externally, including some cullings.
Not archiving, too many. Links are in reverse date order.
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/saudi-arabia-about-confiscate-33-billion-four-its-richest-people
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-06/saudi-banks-begin-freezing-accounts-arrested-royals-block-private-jets
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/06/saudi-purge-sees-senior-princes-top-billionaire-detained/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/05/saudi-energy-minister-falih-says-concerned-about-asias-future-energy-security/
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-05/saudi-helicopter-carrying-8-high-ranking-officials-crown-prince-mansour-crashed-all-
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-05/we%E2%80%99ll-see-some-initial-panic-world-reacts-billionaire-alwaleeds-shocking-purge
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-04/shocking-purge-saudi-king-arrests-billionaire-prince-bin-talal-others-anti-money-lau
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-11-04/lebanon-plunges-uncertainty-after-premier-resigns-fearing-assassination-plot
https://gefira.org/en/2017/11/01/saudi-arabia-may-raise-december-crude-oil-prices-to-asia-to-highest-in-few-years/
https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/international-news/middle_east/saudi-arabia-in-search-of-cash/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/10/24/russia-cements-top-spot-in-crude-sales-to-china-as-saudis-recede/
http://21stcenturywire.com/2017/10/24/syrian-victory-will-reshape-middle-east-recalibrate-global-hegemony/
http://www.thechinamoneyreport.com/2017/10/13/china-will-compel-saudi-arabia-to-trade-oil-in-yuan-and-thats-going-to-affect-the-us-dollar/ <<<<<<<<<<<<<THIS
https://gefira.org/en/2017/10/05/saudi-king-arrives-in-moscow-with-energy-syria-likely-on-agenda/
https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/markets-by-sector/energy/saudi-arabia-threatens-to-privatize-its-oil-and-exit-opec/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/09/27/saudi-arabia-sells-third-international-bond-to-raise-12-5-billion/
https://gefira.org/en/2017/08/28/china-saudi-arabia-agree-to-build-energy-cooperation-mechanisms/
http://www.thechinamoneyreport.com/2017/03/27/chinese-drone-factory-in-saudi-arabia-first-in-middle-east/ <<<<<<China again.
Enough links?
Saudi Arabia might slip the US leash and go to China as China rises.
1510093407.png (283.4 KB, 664x1068, when you try to score with….png)
>>86425
this is what happens when you build the economy of your entire country about a singular increasingly expendable natural resource that can also be purchased somewhere else or replaced with substitutes. What does Saudi Arabia really have besides Oil, sand, camels and a giant gamecube?
this is what happens when you build the economy of your entire country about a singular increasingly expendable natural resource that can also be purchased somewhere else or replaced with substitutes. What does Saudi Arabia really have besides Oil, sand, camels and a giant gamecube?
Saudi Purge Goes Nuclear: Over 1,200 Bank Accounts Frozen
https://archive.is/M5PWZ - ZH
The hunt for money is on. What happens when you deny very rich people their money??
https://archive.is/M5PWZ - ZH
The hunt for money is on. What happens when you deny very rich people their money??
Quote:
The inside story of the Saudi night of long knives
…
The story starts with secret deliberations in 2014 about a possible “removal” of then King Abdullah. But “the dissolution of the royal family would lead to the breaking apart of tribal loyalties and the country splitting into three parts. It would be more difficult to secure the oil, and the broken institutions whatever they were should be maintained to avoid chaos.”
Instead, a decision was reached to get rid of Prince Bandar bin Sultan – then actively coddling Salafi-jihadis in Syria – and replace the control of the security apparatus with Mohammed bin Nayef.
The succession of Abdullah proceeded smoothly. Power was shared between three main clans: King Salman (and his beloved son Prince Mohammed); the son of Prince Nayef (the other Prince Mohammed), and finally the son of the dead king (Prince Miteb, commander of the National Guard). In practice, Salman let MBS run the show.
And, in practice, blunders also followed. The House of Saud lost its lethal regime-change drive in Syria and is bogged down in an unwinnable war on Yemen, which on top of it prevents MBS from exploiting the Empty Quarter – the desert straddling both nations.
The Saudi Treasury was forced to borrow on the international markets. Austerity ruled – with news of MBS buying a yacht for almost half a billion dollars while lazing about the Cote d’Azur not going down particularly well. Hardcore political repression is epitomized by the decapitation of Shi’ite leader Sheikh Al-Nimr. Not only the Shi’ites in the Eastern province are rebelling but also Sunni provinces in the west.
As the regime’s popularity radically tumbled down, MBS came up with Vision 2030. Theoretically, it was shift away from oil; selling off part of Aramco; and an attempt to bring in new industries. Cooling off dissatisfaction was covered by royal payoffs to key princes to stay loyal and retroactive payments on back wages to the unruly masses.
Yet Vision 2030 cannot possibly work when the majority of productive jobs in Saudi Arabia are held by expats. Bringing in new jobs raises the question of where are the new (skilled) workers to come from.
Throughout these developments, aversion to MBS never ceased to grow; “There are three major royal family groups aligning against the present rulers: the family of former King Abdullah, the family of former King Fahd, and the family of former Crown Prince Nayef.”
Nayef – who replaced Bandar – is close to Washington and extremely popular in Langley due to his counter-terrorism activities. His arrest earlier this year angered the CIA and quite a few factions of the House of Saud – as it was interpreted as MBS forcing his hand in the power struggle.
According to the source, “he might have gotten away with the arrest of CIA favorite Mohammed bin Nayef if he smoothed it over but MBS has now crossed the Rubicon though he is no Caesar. The CIA regards him as totally worthless.”
Some sort of stability could eventually be found in a return to the previous power sharing between the Sudairis (without MBS) and the Chamars (the tribe of deceased King Abdullah). After the death of King Salman, the source would see it as “MBS isolated from power, which would be entrusted to the other Prince Mohammed (the son of Nayef). And Prince Miteb would conserve his position.”
MBS acted exactly to prevent this outcome. The source, though, is adamant; “There will be regime change in the near future, and the only reason that it has not happened already is because the old King is liked among his family. It is possible that there may be a struggle emanating from the military as during the days of King Farouk, and we may have a ruler arise that is not friendly to the United States.”
http://archive.fo/scsYl - asia times
The inside story of the Saudi night of long knives
…
The story starts with secret deliberations in 2014 about a possible “removal” of then King Abdullah. But “the dissolution of the royal family would lead to the breaking apart of tribal loyalties and the country splitting into three parts. It would be more difficult to secure the oil, and the broken institutions whatever they were should be maintained to avoid chaos.”
Instead, a decision was reached to get rid of Prince Bandar bin Sultan – then actively coddling Salafi-jihadis in Syria – and replace the control of the security apparatus with Mohammed bin Nayef.
The succession of Abdullah proceeded smoothly. Power was shared between three main clans: King Salman (and his beloved son Prince Mohammed); the son of Prince Nayef (the other Prince Mohammed), and finally the son of the dead king (Prince Miteb, commander of the National Guard). In practice, Salman let MBS run the show.
And, in practice, blunders also followed. The House of Saud lost its lethal regime-change drive in Syria and is bogged down in an unwinnable war on Yemen, which on top of it prevents MBS from exploiting the Empty Quarter – the desert straddling both nations.
The Saudi Treasury was forced to borrow on the international markets. Austerity ruled – with news of MBS buying a yacht for almost half a billion dollars while lazing about the Cote d’Azur not going down particularly well. Hardcore political repression is epitomized by the decapitation of Shi’ite leader Sheikh Al-Nimr. Not only the Shi’ites in the Eastern province are rebelling but also Sunni provinces in the west.
As the regime’s popularity radically tumbled down, MBS came up with Vision 2030. Theoretically, it was shift away from oil; selling off part of Aramco; and an attempt to bring in new industries. Cooling off dissatisfaction was covered by royal payoffs to key princes to stay loyal and retroactive payments on back wages to the unruly masses.
Yet Vision 2030 cannot possibly work when the majority of productive jobs in Saudi Arabia are held by expats. Bringing in new jobs raises the question of where are the new (skilled) workers to come from.
Throughout these developments, aversion to MBS never ceased to grow; “There are three major royal family groups aligning against the present rulers: the family of former King Abdullah, the family of former King Fahd, and the family of former Crown Prince Nayef.”
Nayef – who replaced Bandar – is close to Washington and extremely popular in Langley due to his counter-terrorism activities. His arrest earlier this year angered the CIA and quite a few factions of the House of Saud – as it was interpreted as MBS forcing his hand in the power struggle.
According to the source, “he might have gotten away with the arrest of CIA favorite Mohammed bin Nayef if he smoothed it over but MBS has now crossed the Rubicon though he is no Caesar. The CIA regards him as totally worthless.”
Some sort of stability could eventually be found in a return to the previous power sharing between the Sudairis (without MBS) and the Chamars (the tribe of deceased King Abdullah). After the death of King Salman, the source would see it as “MBS isolated from power, which would be entrusted to the other Prince Mohammed (the son of Nayef). And Prince Miteb would conserve his position.”
MBS acted exactly to prevent this outcome. The source, though, is adamant; “There will be regime change in the near future, and the only reason that it has not happened already is because the old King is liked among his family. It is possible that there may be a struggle emanating from the military as during the days of King Farouk, and we may have a ruler arise that is not friendly to the United States.”
http://archive.fo/scsYl - asia times
1510102110.jpg (486.2 KB, 960x1706, __illyasviel_von_einzbern_….jpg)

>>86522
I have been thinking about that that since the incident with the saudi prince helicopter crash. I would say the National Guard will try to make a power grab, throw over the Royalty of Saudi Arabia and erect a military regime.
I have been thinking about that that since the incident with the saudi prince helicopter crash. I would say the National Guard will try to make a power grab, throw over the Royalty of Saudi Arabia and erect a military regime.
>>86522
>we may have a ruler arise that is not friendly to the United States.
did somebody say free oil?
>we may have a ruler arise that is not friendly to the United States.
did somebody say free oil?
>>86588
I do hope whoever will be in power in Saudi Arabia in the coming years wont be an American Toelicker. It is important to dismantle the Foreign US relations in the middle east and by extension worldwide in order to destoy the US American Imperialism.
I do hope whoever will be in power in Saudi Arabia in the coming years wont be an American Toelicker. It is important to dismantle the Foreign US relations in the middle east and by extension worldwide in order to destoy the US American Imperialism.
35 replies | 23 files | 1 UUIDs | Archived















 Ex: Type :littlepip: to add Littlepip
Ex: Type :littlepip: to add Littlepip  Ex: Type :eqg-rarity: to add EqG Rarity
Ex: Type :eqg-rarity: to add EqG Rarity 