.
/mlpol/ - My Little Politics
Archived thread
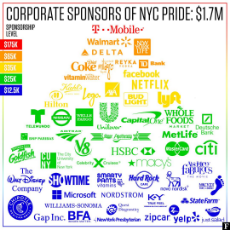
1607316905_2.jpg (205.1 KB, 1080x1080, Corporate sponsors of NYC LGBT Pride Month - (circa 2019).jpg)
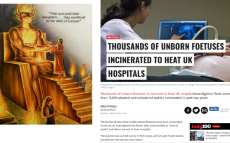
1607317099_3.jpg (34.9 KB, 750x448, millions_abused_by_teachers.jpg)

1607317099_5.jpg (560.9 KB, 1550x970, nhs_child_sacrifice_to_molech.jpg)
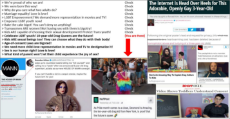
1607317168_2.jpg (207.9 KB, 1431x743, normalization_of_pedophilia.jpg)
1607317168_4.png (641.2 KB, 685x3245, state_enforced_homosexuality.png)

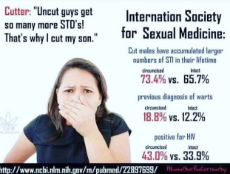
1607317534_2.jpg (374.1 KB, 1097x1097, medical_authorities_circumcision.jpg)

1607317534_5.png (441.3 KB, 800x1370, museum_of_tolerance_gas_van_fraud.png)

1607317815_2.png (873.0 KB, 886x886, israel_does_not_want_peace.png)

1607317815_3.png (47.6 KB, 878x306, israel_knew_iraq_had_no_wmds.png)

1607317845_1.png (593.8 KB, 652x654, Drag_queen_Sisters_of_perpetual_indulgence.png)
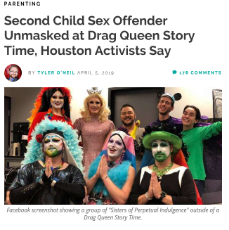
1607317845_2.jpg (99.4 KB, 726x1024, drag_queen_story_time_satanic.jpg)

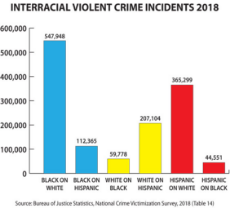
1607318131_4.jpg (126.4 KB, 857x1046, interracial_rape_statistics.jpg)

1607318131_5.jpg (63.7 KB, 549x424, interracial_rape_statistics_2.jpg)

1607318251_4.png (98.9 KB, 711x594, mixed_race_learning_disabilities.png)
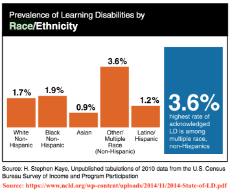
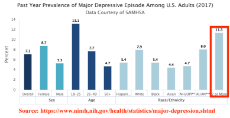
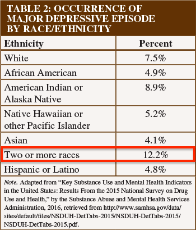
1607318251_5.png (107.8 KB, 1558x800, mixed_race_mental_illness.png)
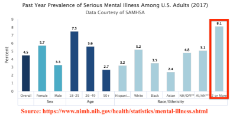
1607318277_1.png (91.1 KB, 1558x800, mixed_race_mental_illness_2.png)
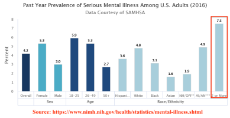
1607318277_2.png (106.9 KB, 1558x800, mixed_race_suicidal_thoughts.png)
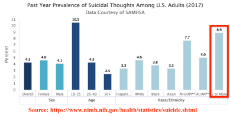
1607318277_3.png (100.9 KB, 1558x800, mixed_race_suicide_attempts.png)
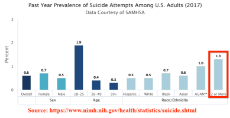
1607318277_5.png (259.5 KB, 500x246, poorest_white_town_richest_black_town.png)

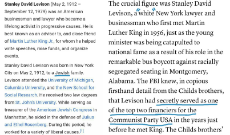
A website was posted here a while back exposing the double standards and blatant contradictions of mainstream news outlets, but I forgot to bookmark it. Who has it bookmarked?
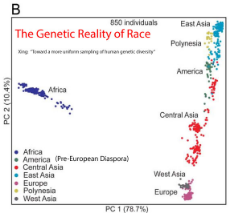
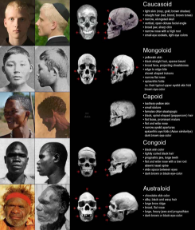
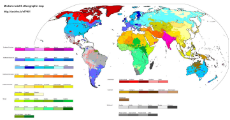
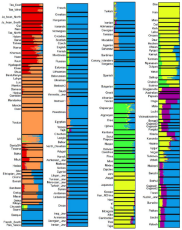
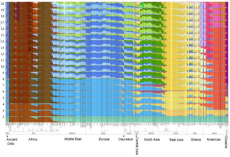
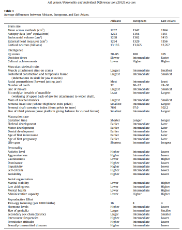
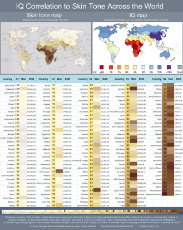
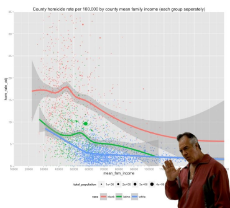
Diversity. Source for the PDF images is here https://thuletide.wordpress.com/2020/08/06/diversity-meta-analysis/
Also: https://thuletide.wordpress.com/2020/06/20/race-and-genetics-part-01/
Last one was made by me. Tell me if theres something to improve real quick
Last one was made by me. Tell me if theres something to improve real quick
https://humanbiologicaldiversity.com/
Thirty years of research on race differences in cognitive ability
https://www1.udel.edu/educ/gottfredson/30years/Rushton-Jensen30years.pdf
Summary: https://rense.com/general77/racedif.htm
Racial Ancestry and IQ
https://ideasanddata.wordpress.com/2019/08/25/racial-ancestry-and-iq/
Cultural group selection plays an essential role in explaining human cooperation: A sketch of the evidence
http://www.des.ucdavis.edu/faculty/Richerson/CGS%20for%20BBS.pdf
Genetic Determinism
https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-16999-6_2162-2
Is Homo sapiens polytypic? Human taxonomic diversity and its implications
https://lesacreduprintemps19.files.wordpress.com/2011/06/woodley-2009-is-homo-sapiens-polytypic-human-taxonomic-diversity-and-its-implications.pdf
Global Ancestry and Cognitive Ability
https://www.mdpi.com/2624-8611/1/1/34/htm
https://twitter.com/KirkegaardEmil/status/1213608667259559937
>Reminder that sizable proportions of social scientists report in private they want to discriminate against conservatives in science.
Brain size, IQ, and racial-group differences: Evidence from musculoskeletal traits
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028960200137X
https://twitter.com/NoahCarl90/status/1213787187281563648
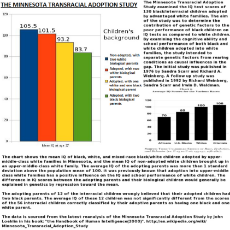
>Two studies have examined the effects of nature versus nurture by exploiting quasi-random assignment of Korean-born adoptees to Western families. For most of the outcomes studied, nature was more important than nurture.
Third Cousins Have Greatest Number Of Offspring, Data From Iceland Shows
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/02/080207140855.htm
Evidence for Recent Polygenic Selection on Educational Attainment and Intelligence Inferred from Gwas Hits: A Replication of Previous Findings Using Recent Data
https://www.mdpi.com/2624-8611/1/1/5
Research on group differences in intelligence: A defense of free inquiry
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09515089.2019.1697803
Adverse perinatal outcomes among interracial couples in the United States.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15994621
Theoretical and empirical quantification of the accuracy of polygenic scores in ancestry divergent populations
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.14.905927v1
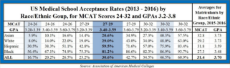
IQ’s Influence on Individual Economic and Educational Success
https://ideasanddata.wordpress.com/2019/08/22/iqs-influence-on-individual-economic-and-educational-success/
https://twitter.com/Sean84076698/status/1218042277492215808
>Feel repetitive, but: most experts think genes are involved in racial IQ disparities, national IQ is predicted by group differences in IQ related gene variants, small increases in European ancestry predict marginal increases in IQ, and the gaps persist after controlling for class
Genomic analysis of family data reveals additional genetic effects on intelligence and personality
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-017-0005-1.pdf
National IQs: A review of their educational, cognitive, economic, political, demographic, sociological, epidemiological, geographic and climatic correlates
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289611001413
Regional Differences in Intelligence in 22 Countries and their Economic, Social and Demographic Correlates: A Review
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028961730212X
The reproduction of intelligence
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/cd82/00efbe1cfa15f76342119fa32cc09ab2a1e2.pdf
Fertility trends by social status
https://www.demographic-research.org/volumes/vol18/5/18-5.pdf
Genetic and Environmental Determinants of IQ in Black, White, and Hispanic Americans: A Meta-analysis and New Analysis
https://humanvarieties.org/2014/09/15/genetic-and-environmental-determinants-of-iq-in-black-white-and-hispanic-americans-a-meta-analysis-and-new-analysis/
Holocene Selection for Variants Associated With General Cognitive Ability: Comparing Ancient and Modern Genomes
https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/BF2A35F0D4F565757875287E59A1F534/S1832427417000378a.pdf/holocene_selection_for_variants_associated_with_general_cognitive_ability_comparing_ancient_and_modern_genomes.pdf
The relationship between cross-national genetic distances and IQ-differences
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S019188691630174X
Haplogroups as evolutionary markers of cognitive ability
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289612000529
Biogeographic Ancestry and Socioeconomic Outcomes in the Americas: A Meta-Analysis
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f322/57e577de12aeb4fb47ce6a33d0d483641064.pdf
Admixture in the Americas: Regional and National Differences
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/298214364_Admixture_in_the_Americas_Regional_and_National_Differences
Thirty years of research on race differences in cognitive ability
https://www1.udel.edu/educ/gottfredson/30years/Rushton-Jensen30years.pdf
Summary: https://rense.com/general77/racedif.htm
Racial Ancestry and IQ
https://ideasanddata.wordpress.com/2019/08/25/racial-ancestry-and-iq/
Cultural group selection plays an essential role in explaining human cooperation: A sketch of the evidence
http://www.des.ucdavis.edu/faculty/Richerson/CGS%20for%20BBS.pdf
Genetic Determinism
https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-16999-6_2162-2
Is Homo sapiens polytypic? Human taxonomic diversity and its implications
https://lesacreduprintemps19.files.wordpress.com/2011/06/woodley-2009-is-homo-sapiens-polytypic-human-taxonomic-diversity-and-its-implications.pdf
Global Ancestry and Cognitive Ability
https://www.mdpi.com/2624-8611/1/1/34/htm
https://twitter.com/KirkegaardEmil/status/1213608667259559937
>Reminder that sizable proportions of social scientists report in private they want to discriminate against conservatives in science.
Brain size, IQ, and racial-group differences: Evidence from musculoskeletal traits
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028960200137X
https://twitter.com/NoahCarl90/status/1213787187281563648
>Two studies have examined the effects of nature versus nurture by exploiting quasi-random assignment of Korean-born adoptees to Western families. For most of the outcomes studied, nature was more important than nurture.
Third Cousins Have Greatest Number Of Offspring, Data From Iceland Shows
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/02/080207140855.htm
Evidence for Recent Polygenic Selection on Educational Attainment and Intelligence Inferred from Gwas Hits: A Replication of Previous Findings Using Recent Data
https://www.mdpi.com/2624-8611/1/1/5
Research on group differences in intelligence: A defense of free inquiry
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09515089.2019.1697803
Adverse perinatal outcomes among interracial couples in the United States.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15994621
Theoretical and empirical quantification of the accuracy of polygenic scores in ancestry divergent populations
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.14.905927v1
IQ’s Influence on Individual Economic and Educational Success
https://ideasanddata.wordpress.com/2019/08/22/iqs-influence-on-individual-economic-and-educational-success/
https://twitter.com/Sean84076698/status/1218042277492215808
>Feel repetitive, but: most experts think genes are involved in racial IQ disparities, national IQ is predicted by group differences in IQ related gene variants, small increases in European ancestry predict marginal increases in IQ, and the gaps persist after controlling for class
Genomic analysis of family data reveals additional genetic effects on intelligence and personality
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-017-0005-1.pdf
National IQs: A review of their educational, cognitive, economic, political, demographic, sociological, epidemiological, geographic and climatic correlates
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289611001413
Regional Differences in Intelligence in 22 Countries and their Economic, Social and Demographic Correlates: A Review
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028961730212X
The reproduction of intelligence
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/cd82/00efbe1cfa15f76342119fa32cc09ab2a1e2.pdf
Fertility trends by social status
https://www.demographic-research.org/volumes/vol18/5/18-5.pdf
Genetic and Environmental Determinants of IQ in Black, White, and Hispanic Americans: A Meta-analysis and New Analysis
https://humanvarieties.org/2014/09/15/genetic-and-environmental-determinants-of-iq-in-black-white-and-hispanic-americans-a-meta-analysis-and-new-analysis/
Holocene Selection for Variants Associated With General Cognitive Ability: Comparing Ancient and Modern Genomes
https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/BF2A35F0D4F565757875287E59A1F534/S1832427417000378a.pdf/holocene_selection_for_variants_associated_with_general_cognitive_ability_comparing_ancient_and_modern_genomes.pdf
The relationship between cross-national genetic distances and IQ-differences
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S019188691630174X
Haplogroups as evolutionary markers of cognitive ability
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289612000529
Biogeographic Ancestry and Socioeconomic Outcomes in the Americas: A Meta-Analysis
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f322/57e577de12aeb4fb47ce6a33d0d483641064.pdf
Admixture in the Americas: Regional and National Differences
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/298214364_Admixture_in_the_Americas_Regional_and_National_Differences
Top 10 Replicated Findings From Behavioral Genetics
https://www.gwern.net/docs/genetics/2016-plomin.pdf
Genetic Structure, Self-Identified Race/Ethnicity, and Confounding in Case-Control Association Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1196372/
Do Those Who Engage In Homosexual Sex More Frequently Rape and Murder The Underage? A Test Of Traditional Morality
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267373956_Do_Those_Who_Engage_In_Homosexual_Sex_More_Frequently_Rape_and_Murder_The_Underage_A_Test_Of_Traditional_Morality
Sexually Antagonistic Selection in Human Male Homosexuality
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0002282
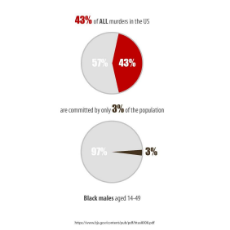
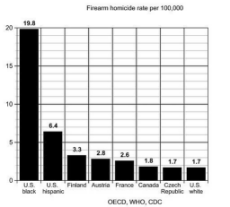
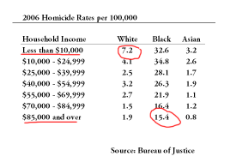
Racial differences in homicide rates are poorly explained by economics
https://randomcriticalanalysis.com/2015/11/16/racial-differences-in-homicide-rates-are-poorly-explained-by-economics/
New MRI Studies Support the Blanchard Typology of Male-to-Female Transsexualism
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3180619/
Genetic Influence on Human Psychological Traits
qute://pdfjs/web/viewer.html?filename=tmp4adfe9mv_bouchard.04.curdir.pdf&file=&source=http://local.psy.miami.edu/faculty/dmessinger/c_c/rsrcs/rdgs/temperament/bouchard.04.curdir.pdf
The association between county-level IQ and county-level crime rates
https://www.gwern.net/docs/iq/2011-beaver.pdf
Sexual orientation and psychiatric vulnerability: a twin study of neuroticism and psychoticism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19588238/
Sub-Saharan African randomised clinical trials into male circumcision and HIV transmission: methodological, ethical and legal concerns.
https://europepmc.org/article/med/22320006
Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26268692
Fat or fiction: the diet-heart hypothesis
https://ebm.bmj.com/content/early/2019/07/10/bmjebm-2019-111180
5 Studies on Saturated Fat — Time to Retire the Myth?
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/5-studies-on-saturated-fat
Hand-grip strength of young men, women and highly trained female athletes
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00421-006-0351-1
https://www.gwern.net/docs/genetics/2016-plomin.pdf
Genetic Structure, Self-Identified Race/Ethnicity, and Confounding in Case-Control Association Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1196372/
Do Those Who Engage In Homosexual Sex More Frequently Rape and Murder The Underage? A Test Of Traditional Morality
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267373956_Do_Those_Who_Engage_In_Homosexual_Sex_More_Frequently_Rape_and_Murder_The_Underage_A_Test_Of_Traditional_Morality
Sexually Antagonistic Selection in Human Male Homosexuality
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0002282
Racial differences in homicide rates are poorly explained by economics
https://randomcriticalanalysis.com/2015/11/16/racial-differences-in-homicide-rates-are-poorly-explained-by-economics/
New MRI Studies Support the Blanchard Typology of Male-to-Female Transsexualism
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3180619/
Genetic Influence on Human Psychological Traits
qute://pdfjs/web/viewer.html?filename=tmp4adfe9mv_bouchard.04.curdir.pdf&file=&source=http://local.psy.miami.edu/faculty/dmessinger/c_c/rsrcs/rdgs/temperament/bouchard.04.curdir.pdf
The association between county-level IQ and county-level crime rates
https://www.gwern.net/docs/iq/2011-beaver.pdf
Sexual orientation and psychiatric vulnerability: a twin study of neuroticism and psychoticism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19588238/
Sub-Saharan African randomised clinical trials into male circumcision and HIV transmission: methodological, ethical and legal concerns.
https://europepmc.org/article/med/22320006
Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26268692
Fat or fiction: the diet-heart hypothesis
https://ebm.bmj.com/content/early/2019/07/10/bmjebm-2019-111180
5 Studies on Saturated Fat — Time to Retire the Myth?
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/5-studies-on-saturated-fat
Hand-grip strength of young men, women and highly trained female athletes
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00421-006-0351-1
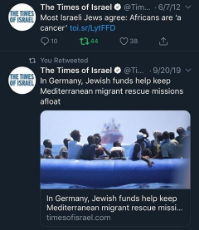
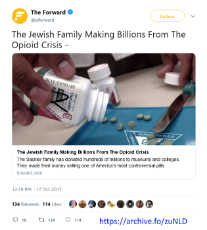
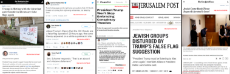
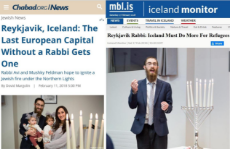
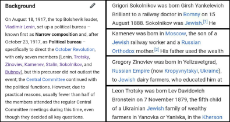
143 Jewish redpills. From Jewish sources.
https://imgur.com/a/isQHClB
https://anonfiles.com/773erax7pb/merchant_zip
https://imgur.com/a/isQHClB
https://anonfiles.com/773erax7pb/merchant_zip
>>293929
https://sci-hub.tw/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1467-9477.2007.00176.x
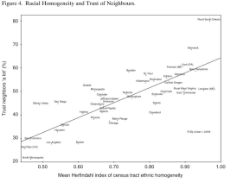
"Inter-racial trust is relatively high in homogeneous South Dakota and relatively low in heterogeneous San Francisco or Los Angeles. The more ethnically diverse the people we live around, the less we trust them. […] the more we are brought into physical proximity with people of another race or ethnic background,the more we stick to ‘our own’ and the less we trust the ‘other"
“Diverse communities tend to be larger, more mobile, less egalitarian, more crime-ridden”
“Within experimental game settings such as prisoners-dilemma or ultimatum games, players who are more different from one another (regardless of whether or not they actually know one another) are more likely to defect (or ‘cheat’).”
https://web.archive.org/web/20160205043520/https://www.msu.edu/~zpneal/publications/neal-diversitysoc.pdf
“Community psychologists are interested in creating contexts that promote both respect for diversity and sense of community. However, recent theoretical and empirical work has uncovered a community-diversity dialectic wherein the contextual conditions that foster respect for diversity often run in opposition to those that foster sense of community. […] integration provides opportunities for intergroup contact that are necessary to promote respect for diversity but may prevent the formation of dense inter-personal networks that are necessary to promote sense of community.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11205-015-0863-3
“In line with the majority of previous studies, we find negative effects of statistical ethnic diversity on each of our five measures of neighborhood social cohesion: trust, collective efficacy, connectedness, reported social problems, and overall satisfaction with neighborhood life. With few
exceptions these effects are statistically significant in all three countries and apply to natives and persons of immigrant origin very much alike.”
https://www.jstor.org/stable/425106?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
“The more ethnic groups in a state, the more likely it will have a high rate of guerrilla and revolutionary warfare. And the more religious groups in a society, the more intense the general violence. This is largely moderated by the size of a state. Thus, the larger and older (counting from 1932) a state in addition to the more religious groups, the more the general violence.”
https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1251240
“Ethnic heterogeneity [diversity] explains 55% of the variation in the scale of ethnic conflicts, and the results of regression analysis disclose that the same relationship more or less applies to all 187 countries. These results led to the conclusion that ethnic nepotism is the common cross-cultural background factor which supports the persistence of ethnic conflicts in the world as long as there are ethnically divided societies.”
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1465-7287.2010.00215.x/abstract
“Using data from U.S. states, I investigate the relationship between ethnic diversity and trust. I find a negative relationship between ethnic polarization and trust […] The main channel through which ethnic diversity is hypothesized to affect trust is social conflict.”
http://www.ifs.org.uk/uploads/publications/wps/WP201530.pdf
“We find that a small minority group will adopt majority cultural practices and integrate. In contrast, minority groups above a certain critical mass, may retain diverse practices and may also segregate from the majority. The size of this critical mass depends on the cultural distance between groups, the importance of culture in day to day life, and the costs of forming a social tie.
http://fivethirtyeight.com/features/the-most-diverse-cities-are-often-the-most-segregated/
“It is all too common to live in a city with a wide variety of ethnic and racial groups — including Chicago, New York, and Baltimore — and yet remain isolated from those groups in a racially homogenous neighborhood. […] the exceptions are cities like Sacramento that have large Hispanic or Asian populations. Cities with substantial black populations tend to be highly segregated. Of the top 100 U.S. cities by population, 35 are at least one-quarter black, and only 6 of those cities have positive integration scores.”
https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/4553003/alesinassrn_fractionalization.pdf?sequence=2
“We concluded that ethnic and linguistic diversity fractionalization variables, but not religious ones, are likely to be important determinants of economic success, both in terms of output (GDP growth), the quality of policies, and the quality of institutions.”
https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/4553005/alesinassrn_ethnicdiversity.pdf?sequence=2
Diversity is negatively associated with economic growth, even after controlling for wealth over time.
https://ils.unc.edu/courses/2013_spring/inls285_001/materials/WIlliams.OReilly.1996.Diversity&demography.pdf
A review of 80 studies spanning 40 years concludes that diversity impedes group functioning and is most likely to cause negative effects.
“Simply having more diversity in a group is no guarantee that the group will make better decisions or function effctively. […] empirical evidence suggests that diversity is most likely to impede group functioning. […] diversity by itself is more likely to have a negative than positive effects on group performance. […] There is substantial evidence from both laboratory and field studies conducted over the past four decades that variations in group composition can have important effects on group functioning. These studies show that increased diversity, especially in terms of age, tenure, and ethnicity, typically have negative effects on social integration, communication, and conflict.”
https://sci-hub.tw/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1467-9477.2007.00176.x
"Inter-racial trust is relatively high in homogeneous South Dakota and relatively low in heterogeneous San Francisco or Los Angeles. The more ethnically diverse the people we live around, the less we trust them. […] the more we are brought into physical proximity with people of another race or ethnic background,the more we stick to ‘our own’ and the less we trust the ‘other"
“Diverse communities tend to be larger, more mobile, less egalitarian, more crime-ridden”
“Within experimental game settings such as prisoners-dilemma or ultimatum games, players who are more different from one another (regardless of whether or not they actually know one another) are more likely to defect (or ‘cheat’).”
https://web.archive.org/web/20160205043520/https://www.msu.edu/~zpneal/publications/neal-diversitysoc.pdf
“Community psychologists are interested in creating contexts that promote both respect for diversity and sense of community. However, recent theoretical and empirical work has uncovered a community-diversity dialectic wherein the contextual conditions that foster respect for diversity often run in opposition to those that foster sense of community. […] integration provides opportunities for intergroup contact that are necessary to promote respect for diversity but may prevent the formation of dense inter-personal networks that are necessary to promote sense of community.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11205-015-0863-3
“In line with the majority of previous studies, we find negative effects of statistical ethnic diversity on each of our five measures of neighborhood social cohesion: trust, collective efficacy, connectedness, reported social problems, and overall satisfaction with neighborhood life. With few
exceptions these effects are statistically significant in all three countries and apply to natives and persons of immigrant origin very much alike.”
https://www.jstor.org/stable/425106?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
“The more ethnic groups in a state, the more likely it will have a high rate of guerrilla and revolutionary warfare. And the more religious groups in a society, the more intense the general violence. This is largely moderated by the size of a state. Thus, the larger and older (counting from 1932) a state in addition to the more religious groups, the more the general violence.”
https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1251240
“Ethnic heterogeneity [diversity] explains 55% of the variation in the scale of ethnic conflicts, and the results of regression analysis disclose that the same relationship more or less applies to all 187 countries. These results led to the conclusion that ethnic nepotism is the common cross-cultural background factor which supports the persistence of ethnic conflicts in the world as long as there are ethnically divided societies.”
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1465-7287.2010.00215.x/abstract
“Using data from U.S. states, I investigate the relationship between ethnic diversity and trust. I find a negative relationship between ethnic polarization and trust […] The main channel through which ethnic diversity is hypothesized to affect trust is social conflict.”
http://www.ifs.org.uk/uploads/publications/wps/WP201530.pdf
“We find that a small minority group will adopt majority cultural practices and integrate. In contrast, minority groups above a certain critical mass, may retain diverse practices and may also segregate from the majority. The size of this critical mass depends on the cultural distance between groups, the importance of culture in day to day life, and the costs of forming a social tie.
http://fivethirtyeight.com/features/the-most-diverse-cities-are-often-the-most-segregated/
“It is all too common to live in a city with a wide variety of ethnic and racial groups — including Chicago, New York, and Baltimore — and yet remain isolated from those groups in a racially homogenous neighborhood. […] the exceptions are cities like Sacramento that have large Hispanic or Asian populations. Cities with substantial black populations tend to be highly segregated. Of the top 100 U.S. cities by population, 35 are at least one-quarter black, and only 6 of those cities have positive integration scores.”
https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/4553003/alesinassrn_fractionalization.pdf?sequence=2
“We concluded that ethnic and linguistic diversity fractionalization variables, but not religious ones, are likely to be important determinants of economic success, both in terms of output (GDP growth), the quality of policies, and the quality of institutions.”
https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/4553005/alesinassrn_ethnicdiversity.pdf?sequence=2
Diversity is negatively associated with economic growth, even after controlling for wealth over time.
https://ils.unc.edu/courses/2013_spring/inls285_001/materials/WIlliams.OReilly.1996.Diversity&demography.pdf
A review of 80 studies spanning 40 years concludes that diversity impedes group functioning and is most likely to cause negative effects.
“Simply having more diversity in a group is no guarantee that the group will make better decisions or function effctively. […] empirical evidence suggests that diversity is most likely to impede group functioning. […] diversity by itself is more likely to have a negative than positive effects on group performance. […] There is substantial evidence from both laboratory and field studies conducted over the past four decades that variations in group composition can have important effects on group functioning. These studies show that increased diversity, especially in terms of age, tenure, and ethnicity, typically have negative effects on social integration, communication, and conflict.”
>>294505
Have you ever tried jewsoap?
Have you ever tried jewsoap?
with that. also kys.
Bump.
the last pic is a hoax, it clearly depicts a white woman, and never on this earth a mix of all races would look like that
New thread was moved to this thread per rule 11.
Bumping.
This old lady is a deluge of redpills, non stop she names the jew.
>Dr. Lorraine Day Nails It!
https://www.bitchute.com/video/kCrX6VZj6ua4/
>Dr. Lorraine Day Nails It!
https://www.bitchute.com/video/kCrX6VZj6ua4/
66 replies | 253 files | 9 UUIDs | Archived



















































































































































 Ex: Type :littlepip: to add Littlepip
Ex: Type :littlepip: to add Littlepip  Ex: Type :eqg-rarity: to add EqG Rarity
Ex: Type :eqg-rarity: to add EqG Rarity 